RESEARCH PROGRESS OF QUATERNARY ENVIRONMENT OF BADAIN JARAN DESERT
-
摘要:
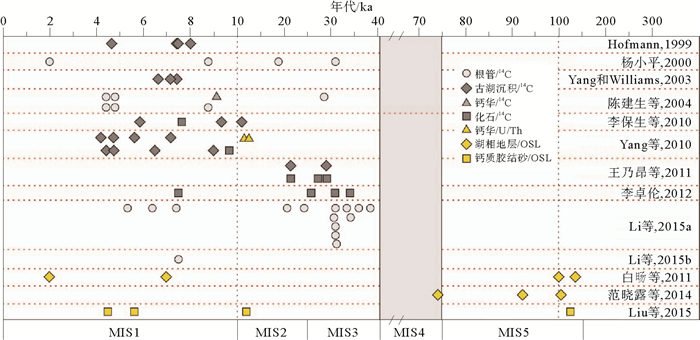
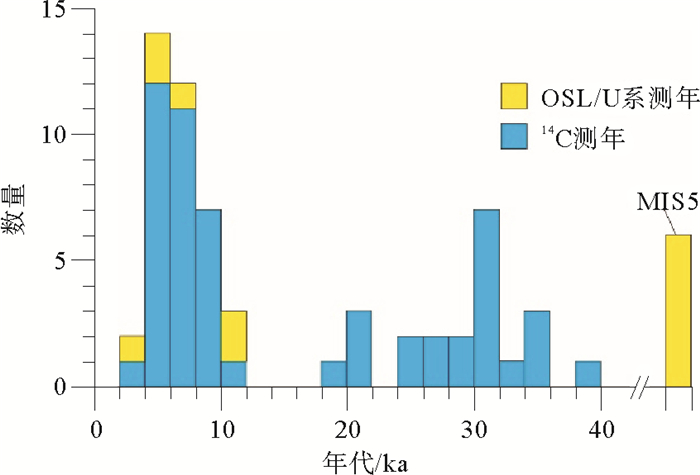
巴丹吉林沙漠第四纪环境研究一直是第四纪地质学、水文地质学研究和关注的热点。目前,巴丹吉林沙漠地区第四纪环境研究对象主要为钙质根管、钙质胶结砂、古湖沉积和少量的钻孔、剖面。已有的研究成果表明,巴丹吉林沙漠在第四纪存在4个湿润阶段:MIS13-15、MIS5、MIS3?、早中全新世。分析已有的研究成果,认为在是否存在MIS3湿润阶段、14C测年精度和钙质根管、钙质胶结砂成因方面还存在不足。为了更好地解决巴丹吉林沙漠形成、湖水咸化等第四纪地质、水文地质问题,建议加强连续、长时间尺度的钻孔、湖泊沉积研究。
Abstract:The Badain Jaran desert, located in west China, is the third largest desert in China and the only one in which megadunes are densely distributed. There are also hundreds of lakes in the desert. Quaternary environment evolution of the desert was controlled by the East Asia monsoon, which renders significant influence on the formation and evolution of the megadunes and lakes. Therefore, the Quaternary environment of the desert has always been a hot topic of debate, especially among the Quaternary and Hydrology researchers. In this paper we reviewed previous studies with emphasis on the calcareous rhizolith, calcareous layers, and lacustrine sediments formed in humid environment. A few drilling cores and stratigraphic sections are studied. Previous studies indicate that there are four humid phases, in MIS13-15, MIS5, MIS3? and the early and middle Holocene respectively in the Badain Jaran desert. In the existing studies, little is known about the existence of MIS3, the accuracy of 14C dating and the origin of rhizolith and calcareous layers. For better dealing with the desert formation, lake salinization, as well as other Quantary and hydro-geological problems in the Badain Jaran Desert, we suggest strengthening continuous and long-term researches on the drill core and lacustrine deposits.
-
Key words:
- environmental records /
- research progress /
- Quaternary /
- Badain Jaran desert
-

-
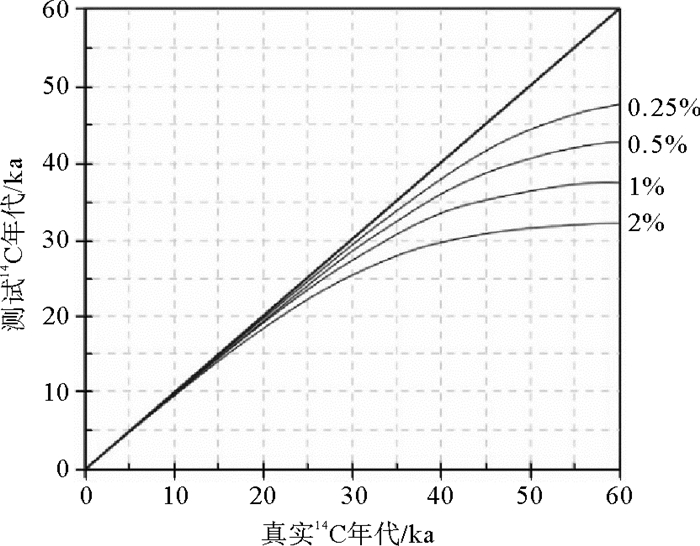
图 4 不同程度的现代碳污染对14C测年结果的影响[64]
Figure 4.
-
[1] Yang X, Liu T, Xiao H. Evolution of megadunes and lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert, Inner Mongolia, China during the last 31, 000 years[J]. Quaternary International, 2003, 104(1): 99-112. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(02)00138-6
[2] Andreotti B, Fourrière A, Ould-Kaddour F, et al. Giant aeolian dune size determined by the average depth of the atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7233): 1120-1123. doi: 10.1038/nature07787
[3] Dong Z, Qian G, Lv P, et al. Investigation of the sand sea with the tallest dunes on Earth: China's Badain Jaran Sand Sea[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 120: 20-39. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.02.003
[4] 丁宏伟, 郭瑞, 田刚, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊与高大沙山形成的若干问题探讨[J].甘肃地质, 2015, 24(2): 9-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsdzxb201502002
DING Hongwei, GUO Rui, TIAN Gang, et al. Formation and evolution of lakes and sand hills in the Badain Jaran desert, China[J]. Gansu Geology, 2015, 24(2): 9-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsdzxb201502002
[5] Yang X, Scuderi L, Liu T, et al. Formation of the highest sand dunes on Earth[J]. Geomorphology, 2011, 135(1-2): 108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.08.008
[6] Chen J S, Li L, Wang J Y, et al. Water resources - Groundwater maintains dune landscape[J].Nature, 2004, 432(7016): 459-460. doi: 10.1038/432459a
[7] Ma J Z, Ding Z, Gates J B, et al. Chloride and the environmental isotopes as the indicators of the groundwater recharge in the Gobi Desert, northwest China[J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 55(7): 1407-1419. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-1091-1
[8] Yang X, Ma N, Dong J, et al. Recharge to the inter-dune lakes and Holocene climatic changes in the Badain Jaran desert, western China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73(1): 10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.10.009
[9] 郭永海, 王海龙, 董建楠, 等.关于巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊形成机制的初步看法[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(2): 276-282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201202009
GUO Yonghai, WANG Hailong, DONG Jian-nan, et al. The primary opinion on the formation mechanisms of megadunes and lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geoscience, 2012, 37(2): 276-282. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201202009
[10] Yang X, Williams M A J. The ion chemistry of lakes and late Holocene desiccation in the Badain Jaran Desert, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. CATENA, 2003, 51(1): 45-60. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(02)00088-7
[11] Liu S, Lai Z, Wang Y, et al. Growing pattern of mega-dunes in the Badain Jaran Desert in China revealed by luminescence ages[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 410: 111-118. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=02e121e6b623a1ce2ee75e514883390a
[12] Wang F, Sun D, Chen F, et al. Formation and evolution of the Badain Jaran desert, north China, as revealed by a drill core from the desert centre and by geological survey[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2015, 426: 139-158. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.03.011
[13] 杨小平.近3万年来巴丹吉林沙漠的景观发育与雨量变化[J].科学通报, 2000, 45(4): 428-434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.04.020
YANG Xiaoping. Landscape development and rainfall change in the Badain Jaran desert since approximately 30 kaBP[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(4): 428-434. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.04.020
[14] 白旸, 王乃昂, 何瑞霞, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖相沉积的探地雷达图像及光释光年代学证据[J].中国沙漠. 2011, 31(4): 842-847. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201104006
BAI Yang, WANG Nai-ang, HE Rui-xia, et al. Ground penetrating radar images and optically stimulated luminescence dating for lacustrine Deposition of the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2011, 31(4): 842-847. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201104006
[15] 范小露, 田明中, 刘斯文.巴丹吉林沙漠东南部末次间冰期环境演变:来自粒度、光释光(OSL)及14C测年的证据[J].干旱区地理, 2014, 37(5): 892-900. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqdl201405004
FAN Xiaolu, TIAN Mingzhong, LIU Siwen. Environmental change of southeastern Badain Jaran Desert during the last interglacial: evidences from the grain-size analysis, optically stimulated luminescence and radiocarbon dating[J]. Arid Land Geology, 2014, 37(5): 892-900. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqdl201405004
[16] 安芷生, 张培震, 王二七, 等.中新世以来我国季风-干旱环境演化与青藏高原的生长[J].第四纪研究. 2006, 26(5): 678-693. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.05.002
AN Zhisheng, ZHANG Peizhen, WANG Erqi, et al. Changes of the monsoon-arid environment in China and grow of the Tibetan Plateau since the Miocene[J]. Quaternary Science, 2006, 26(5): 678-693. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.05.002
[17] Wright V P, Tucker M E. Rhizoliths in Terrestrial Carbonates: Classification, Recognition, Genesis and Significance[M]. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2009: 149-165.
[18] Gocke M, Pustovoytov K, Kühn P, et al. Carbonate rhizoliths in loess and their implications for paleoenvironmental reconstruction revealed by isotopic composition: δ13C, 14C[J]. Chemical Geology, 2011, 283(3): 251-260. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.01.022
[19] Jones B N K C. The structure and diagenesis of rhizolites from Cayman Brac, British West Indies[J]. Sediment Petrol, 1988(58): 457-467.
[20] Cerling T E. The stable isotopic composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationship to climate[J]. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 1984(71): 229-240. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1177/030913337800200301
[21] Birkeland P W. Soils and Geomorphology[M]. Oxford University Press, 1984.
[22] Liu Z. Plant root tube fossils in the south region of the Badain Jaran desert, Inner Mongolia, China, and their paleo-environmental interpretations[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 347: 284-285. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2012.08.749
[23] Li Z, Wang N, Cheng H, et al. Formation and environmental significance of late Quaternary calcareous root tubes in the deserts of the Alashan Plateau, northwest China[J]. Quaternary International, 2015, 372: 167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.11.021
[24] Li Z, Wang N, Li R, et al. Indication of millennial-scale moisture changes by the temporal distribution of Holocene calcareous root tubes in the deserts of the Alashan Plateau, Northwest China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2015, 440: 496-505. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.09.023
[25] 杨小平.巴丹吉林沙漠地区钙质胶结层的发现及其古气候意义[J].第四纪研究, 2000, 20(3): 295-297. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.03.010
YANG Xiaoping. Discovery of calcareous cementation layers and their paleoclimatic implications in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2000, 20(3): 295-297. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2000.03.010
[26] 陈建生, 赵霞, 汪集旸, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊钙华与根状结核的发现对研究湖泊水补给的意义[J].中国岩溶, 2004, 23(4): 21-26. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyr200404004
CHEN Jiansheng, ZHAO Xia, WANG Jiyang, et al. Meaning of the discovery of lacustrine tufa and root-shaped nodule in Badain Jaran Desert for the study on lake recharge[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2004, 23(4): 21-26. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyr200404004
[27] Mischke Steffen.内蒙古巴丹吉林沙漠成因的粒度分析和热发光测年新证据[J].古地理学报, 2005, 7(1): 79-97. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb200501008
Meischke S. New evidence for origin of Badain Jaran Desert of Inner Mongolia from granulometry and thermoluminescence dating[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2005, 7(1): 79-97. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdlxb200501008
[28] 李卓伦.巴丹吉林沙漠及周边地区晚第四纪湖泊年代学与气候背景[D].兰州大学, 2012.
LI Zhuolun. Paleolake chronology and climate background on Badain Jaran Desert and its marginal area during the Late Quaternary[D]. Lanzhou University, 2012.
[29] 王乃昂, 李卓仑, 程弘毅, 等.阿拉善高原晚第四纪高湖面与大湖期的再探讨[J].科学通报. 2011, 56(17): 1367-1377. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1038-sc.2009.139/
WANG Naiang, LI Zhuolun, CHENG Hongyi, et al. High lake levels on Alashan Plateau during the Late Quaternary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(17): 1367-1377. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1038-sc.2009.139/
[30] J H. Geökologische Untersuchungen derGewässer im Südosten der Badain Jaran Wüste (Aut. Region Innere Mongolei/VR China)-Status und Spätquartäre Gewässerentwicklung[M]. 1999.
[31] 董光荣, 高全洲, 邹学勇, 等.晚更新世以来巴丹吉林沙漠南缘气候变化[J].科学通报, 1995, 40(13): 1214-1218. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb199513018
DONG Guangrong, GAO Quanzhou, ZOU Xueyong, et al. Climate changes at southern fringe of the Badain Jaran desert since Pleistocene[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(13): 423-427. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb199513018
[32] 高全洲, 董光荣, 李保生, 等.晚更新世以来巴丹吉林南缘地区沙漠演化[J].中国沙漠, 1995, 15(4): 345-352. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.1995.04.014
GAO Quanzhou, DONG Guangrong, LI Baosheng, et al. Evolution of southern fringe of Badain Jaran Desert since Late Pleistocene[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 1995, 15(4): 345-352. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.1995.04.014
[33] 高全洲, 陶贞, 董光荣, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠查格勒布鲁剖面的沉积地球化学特征[J].地理学报, 1998(S1): 44-51. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxb1998z1006
GAO Quanzhou, TAO Zhen, DONG Guangrong, et al. The characteristics of sediments geochemistry in Chagelebulu Section in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1998(Sl): 44-51. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dlxb1998z1006
[34] 高全洲, 陶贞, 董光荣.微量元素记录的化学风化和气候变化:以巴丹吉林沙漠查格勒布鲁剖面为例[J].中国沙漠, 2001, 21(4): 374-379. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2001.04.010
GAO Quanzhou, TAO Zhen, DONG Guangrong. Chemical weathering and climate changes recorded by the trace elements in Chagelebulu Section, Badain Jaran Desert, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2001, 21(4): 374-379. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2001.04.010
[35] 李云卓, 李保生, 高全洲, 等.巴丹吉林查格勒布剖面记录的150 kaBP以来的常量化学元素波动[J].中国沙漠, 2005, 25(1): 8-14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2005.01.002
LI Yunzhuo, LI Baosheng, GAO Quanzhou, et al. Fluctuations of main chemical elements since 150 kaBP as indicated in Chagelebulu stratigraphical Section, Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2005, 25(1): 8-14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2005.01.002
[36] 李保生, 高全洲, 阎满存, 等. 150 kaBP以来巴丹吉林沙漠东南区域地层序列的新研究[J].中国沙漠, 2005, 25(4): 457-465. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2005.04.002
LI Baosheng, GAO Quanzhou, YAN Mancun et al. A recent study on sedimentary sequence of southeastern Badain Jaran Desert since 150 kaBP[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2005, 25(4): 457-465. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2005.04.002
[37] 杨艺, 李保生, 李云卓, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠查格勒布剖面微量元素反映的150kaBP以来的气候变化[J].中国沙漠, 2007, 27(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2007.01.007
YANG Yi, LI Baosheng, LI Yunzhuo, et al. Palaeo-Climate change indicated from fluctuations of trace elements since 150 kaBP in Chagelebulu Stratigraphical Section, Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(1): 1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2007.01.007
[38] Yang Y, Li B S, Qiu S F, et al. Climatic changes indicated by trace elements in the Chagelebulu Stratigraphic Section, Badain Jaran Desert, China, since 150 kaBP[J]. Geochemistry International, 2008, 46(1): 96-103. doi: 10.1134/S0016702908010096
[39] 郭亿华, 李保生, 温小浩, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠东南缘查格勒布鲁剖面CGS1层段粒度特征及其指示的全新世千年尺度气候变化[J].中国沙漠, 2012, 32(5): 1248-1255. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201205010
GUO Yihua, LI Baosheng, WEN Xiaohao, et al. Holocene climate variations on Millennium-scale from grain-size record of CGS1 segment in the Badain Jaran Desert, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2012, 32(5): 1248-1255. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201205010
[40] Guo Y, Li B, Wen X, et al. Holocene climate variation determined from rubidium and strontium contents and ratios of sediments collected from the BadainJaran Desert, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chemie der Erde - Geochemistry, 2014, 74(4): 571-576. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2013.09.001
[41] Gao Q, Tao Z, Li B, et al. Palaeomonsoon variability in the southern fringe of the Badain Jaran Desert, China, since 130 kaBP[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2006, 31(3): 265-283. doi: 10.1002/esp.1242
[42] 马金珠, 陈发虎, 赵华. 1 000年以来巴丹吉林沙漠地下水补给与气候变化的包气带地球化学记录[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(1): 22-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.01.004
MA Jinzhu, CHEN Fahu, ZHAO Hua. Change on climate change and groundwater recharge from geochemical records of unsaturated zone in the Badain Jaran Desert in the recent 1 000 years[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(1): 22-27. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.01.004
[43] Ma J, Edmunds W M. Groundwater and lake evolution in the Badain Jaran desert ecosystem, Inner Mongolia[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2006, 14(7): 1231-1243. doi: 10.1007/s10040-006-0045-0
[44] Gates J B, Edmunds W M, Ma J, et al. A 700-Year history of groundwater recharge in the Drylands of NW China[J]. Holocene, 2008, 18(7): 1045-1054. doi: 10.1177/0959683608095575
[45] Ma J, Edmunds W M, He J, et al. A 2000 year geochemical record of palaeoclimate and hydrology derived from dune sand moisture[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 2009, 276(1-4): 38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2009.02.028
[46] Xiao S C, Xiao H L, Dong Z B, et al. Dry/wet variation recorded by shrub tree-rings in the central Badain Jaran Desert of northwestern China[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2012, 87(87): 85-94. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a542b204dcca0a7f7b917d64972a75f4
[47] Guo Y, Li B, Wang F, et al. Holocene millennial-scale climate variations from the record of primary chemical elements in Badain Jaran Desert, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2016, 9(1): 1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=74bef3c71cbff6eaf4671fa3541f67c2
[48] 马宁, 王乃昂, 朱金峰, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠周边地区近50 a来气候变化特征[J].中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6): 1541-1547. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201106030
MA Ning, WANG Naiang, ZHU Jinfeng, et al. Climate change around the Badain Jaran Desert in Recent 50 years[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2011, 31(6): 1541-1547. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsm201106030
[49] 陈发虎, 范育新, 春喜, 等.晚第四纪"吉兰泰-河套"古大湖的初步研究[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(10): 1207-1219. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.10.013
CHEN Fahu, FAN Yuxin, CHUN Xi, et al. The preliminary study on the Jilantai-Hetao Great Lake of late Quaternary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(10): 1207-1219. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.10.013
[50] Madsen D B, Haizhou M, Rhode D, et al. Age constraints on the late Quaternary evolution of Qinghai Lake, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Research, 2008, 69(2): 316-325. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2007.10.013
[51] Rhode D, Haizhou M, Madsen D B, et al. Paleoenvironmental and archaeological investigations at Qinghai Lake, western China: Geomorphic and chronometric evidence of lake level history[J]. Quaternary International, 2010, 218(1-2): 29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2009.03.004
[52] Madsen D B, Lai Z, Sun Y, et al. Late Quaternary Qaidam lake histories and implications for an MIS 3 "Greatest Lakes" period in northwest China[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2014, 51(2): 161-177. doi: 10.1007/s10933-012-9662-x
[53] Long H, Lai Z, Fuchs M, et al. Timing of late Quaternary palaeolake evolution in Tengger desert of northern China and its possible forcing mechanisms[J]. Global and Planetary Change. 2012, 92-93: 119-129. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.05.014
[54] 隆浩, 沈吉.青藏高原及其邻区晚更新世高湖面事件的年代学问题——以柴达木盆地和腾格里沙漠为例[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 45(1): 52-65. doi: 10.1360/zd-2015-45-1-52
LONG Hao, SHEN Ji. Underestimated 14C-based chronology of late Pleistocene high lake-level events over the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent areas: Evidence from the Qaidam Basin and Tengger Desert[J]. Scicence China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 45(1): 183-194. doi: 10.1360/zd-2015-45-1-52
[55] Yang X, Scuderi L A. Hydrological and climatic changes in deserts of China since the late Pleistocene[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 73(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.10.011
[56] 李保生, Hofmann Jürgen, 陈德牛, 等.全新世大暖期时中国夏季风向西北大幅度漂移的一个古生物地层学证据[J].地球环境学报, 2010, 1(2): 133-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhjxb201002008
LI Baosheng, Hofmann Jürgen, CHEN Deniu, et al. A bio-stratigraphy evidence of summer monsoon drift on a large scale toward NW China during the Holocene Megathermal[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2010, 1(2): 133-138. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhjxb201002008
[57] Xiao S C, Xiao H L, Dong Z B, et al. Dry/wet variation recorded by shrub tree-rings in the central Badain Jaran Desert of northwestern China[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2012, 87: 85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2012.06.013
[58] Lai Z, Mischke S, Madsen D. Paleoenvironmental implications of new OSL dates on the formation of the "Shell Bar" in the Qaidam Basin, northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2014, 51(2): 197-210. doi: 10.1007/s10933-013-9710-1
[59] Chen K, Bowler J M. Late Pleistocene evolution of salt lakes in Qaidam Basin, Quinghai Province, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1986, 54(1-4): 87-104. doi: 10.1016/0031-0182(86)90119-7
[60] Pachur H J, Wünnemann B, Zhang H. Lake evolution in the Tengger Desert, northwestern China, during the Last 40, 000 years[J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2): 171-180. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1061
[61] Zhang L Y H C. AMS dating on the shell bar section from Qaidam Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Radiocarbon, 2008, 50(2): 255-265. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200033555
[62] Long H, Lai Z, Wang N, et al. Holocene climate variations from Zhuyeze terminal lake records in East Asian monsoon margin in arid northern China[J]. Quaternary Research, 2010, 74(1): 46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2010.03.009
[63] Song Y, Lai Z, Li Y, et al. Comparison between luminescence and radiocarbon dating of late Quaternary loess from the Ili Basin in Central Asia[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2015, 30: 405-410. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.01.012
[64] Pigati J S, Quade J, Wilson J, et al. Development of low-background vacuum extraction and graphitization systems for 14C dating of old (40-60 ka) samples[J]. Quaternary International, 2007, 166(1): 4-14. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2006.12.006
[65] Garzione C N, Dettman D L, Horton B K. Carbonate oxygen isotope paleoaltimetry: evaluating the effect of diagenesis on paleoelevation estimates for the Tibetan plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2004, 212(1-2): 119-140. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(04)00307-4
[66] Webb G E, Price G J, Nothdurft L D, et al. Cryptic meteoric diagenesis in freshwater bivalves:Implications for radiocarbon dating[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(9): 803-806. doi: 10.1130/G23823A.1
[67] Hofmann J G M. Untersuchungen zum 14C-resservior effect an rezenten und fossilen lakestrinen Sediments aus dem Südosten der Badain Jaran Wüste (Innere Mongolei/VR China)[J]. Berliner geographische Abhandlugen, 1998(63): 83-89.
[68] Zhou A F, Chen F H, Wang Z L, et al. Temporal change of radiocarbon reservoir effect in Sugan Lake, northwest China during the late Holocene[J]. Radiocarbon, 2009, 51(2): 529-535. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200055909
[69] Wang J, Zhu L, Wang Y, et al. Variability of the 14C reservoir effects in Lake Tangra Yumco, Central Tibet (China), determined from recent sedimentation rates and dating of plant fossils[J]. Quaternary International, 2015. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddc8ca9630879a7c07f63aeabe9cf92b
[70] 王宗礼, 何建华, 陈亚东.湖泊碳库效应及校正方法[J].中国沙漠, 2014, 34(3): 683-688. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201403009
WANG Zongli, HE Jianhua, CHEN Yadong. The reservoir effect of radiocarbon dating in lake sediment system[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2014, 34(3): 683-688. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsm201403009
[71] Wang N A, Li Z, Li Y, et al. Younger Dryas event recorded by the mirabilite deposition in Huahai lake, Hexi Corridor, NW China[J]. Quaternary International, 2012, 250: 93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.11.017
[72] Long H, Lai Z P, Wang N A, et al. A combined luminescence and radiocarbon dating study of Holocene lacustrine sediments from arid northern China[J]. Quatemary Geochronology, 2011, 6(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2010.06.001
[73] Liutkus C M, Wright J D, Ashley G M, et al. Paleoenvironmental interpretation of lake-margin deposits using δ13C and δ18O results from early Pleistocene carbonate rhizoliths, Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(5): 377. doi: 10.1130/G21132.1
[74] 马宁, 王乃昂, 赵力强, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠腹地降水事件后的沙山蒸发观测[J].科学通报, 2014, 59(7): 615-622. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201407009
MA Ning, WANG Nai-ang, ZHAO Liqiang, et al. Observation of mega-dune evaporation after various rain events in the hinterland of Badain Jaran desert[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(7): 615-622. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201407009
[75] An C, Feng Z, Barton L. Dry or humid? Mid-Holocene humidity changes in arid and semi-arid China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(3-4): 351-361. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2005.03.013
[76] Wang W, Ma Y, Feng Z, et al. A prolonged dry mid-Holocene climate revealed by pollen and diatom records from Lake Ugii Nuur in central Mongolia[J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 229(1-2): 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2010.06.005
[77] Dong Z, Wang T, Wang X. Geomorphology of the megadunes in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Geomorphology, 2004, 60(1): 191-203. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8468efc81f7cb9a97aaacac9569024dd
[78] 丁宏伟, 王贵玲.巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊形成的机理分析[J].干旱区研究, 2007, 24(1): 1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqyj200701001
DING Hongwei, WANG Guiling. Study on the formation mechanism of the lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2007, 24(1): 1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ghqyj200701001
[79] 陈建生, 赵霞, 盛雪芬, 等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊群与沙山形成机理研究[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(23): 2789-2796. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.23.014
CHEN Jiansheng, ZHAO Xia, SHENG Xuefen, et al. Research on formation mechanism of megadunes and lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(23): 2789-2796. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.23.014
[80] 王涛.巴丹吉林沙漠形成演变的若干问题[J].中国沙漠, 1990, 10(1): 29-40. http://www.desert.ac.cn/CN/Y1990/V10/I1/29
WANG Tao. Some problems on the formation and evolution of Badain Jaran desert[J]. Journal of Chinese Desert Research, 1990, 10(1): 29-40. http://www.desert.ac.cn/CN/Y1990/V10/I1/29
[81] 黄天明, 庞忠和.应用环境示踪剂探讨巴丹吉林沙漠及古日乃绿洲地下水补给[J].现代地质. 2007, 21(4): 624-631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.006
HUANG Tianming, PANG Zhonghe. Groundwater recharge in Badain Jaran Desert and Gurinai Oasis based on environmental tran cers[J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(4): 624-631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.006
[82] Li Z, Sun D, Chen F, et al. Chronology and paleoenvironmental records of a drill core in the central Tengger Desert of China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 85: 85-98. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.12.003
[83] Z A, Sm C, W Z, et al. Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2(8): 1036. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3431539
-




 下载:
下载: